Task 1- relative sizes and Distances of the planets in the Solar System
- Task 1a- The Relative sizes of the planets
- Look at the Example
- Using the Data table Select the best scale for drawing the diagram (you can use A3 or A4 plain paper)
- Accurately draw your own version of the diagram
- Colour and label the diagram
- Do some research and add some information about the planets (like temperature, length of day length of year no of moons etc)
- Evaluate your work (say how the task went, what mistakes you made, how you corrected them, was it more difficult than you anticipated, are you pleased with the result)
-
Task 1b- The Relative Distances of the planets
- Look at the example provided for you
- Choose an appropriate scale from the data table . You can do EITHER the distances from Earth OR the distances from the sun.
Bear in mind that you CAN stick several pieces together for this task (as shown below)

- Complete the diagram ACCURATELY, LABEL it, Mark on the Distances
- Draw and colour the planets OR print off some pictures and stick them on
- Record the scale distances you have used
- On the bottom of your diagram write the answer to this question "What do YOU notice about the relative distances between the planets?"
- Evaluate your work
Task 2- The Big Bang Theory
- Task 2a -The Big Bang Theory
Big bang source 1
Big bang source 2 (word doc)
Big bang source 3
Big Bang interactive journey (link)
you must include the following information:Big bang source 2 (word doc)
Big bang source 3
Big Bang interactive journey (link)
- What IS the big bang Theory (what does it explain)
- How the Universe has developed since the Big Bang theory (include information on quarks, formation of atoms, the expansion and cooling of the universe)
- What are the 3 possible futures of the Universe
- What information have scientists used to come up with this theory?
- A diagram summarising the Big Bang theory
- Evaluate your work
-
1) Explain (with the aid of a diagram) how the Frequency of waves changes as an object moves towards or away from a wave
- Evaluate your work
2) What is the Doppler effect
3) Why does an ambulance sound different to a person when it is coming towards them than when it is going away?
4) What happens to a light wave if you change its frequency?
5) Why does a star that is moving away from you appear redder than it really is
Task 3- The Life Cycle of a star
For this you must produce a cartoon, story or essay (on 1 side of A4 paper) chronicling the life Cycle of a star.
Use the following information to help
Your cartoon, story or essay must include the following information
- The role of gravity in producing Nuclear fusion that gives birth to a star
- The impact a stars mass has on it's colour and life span
- How stars of different masses die
- Evaluate your work
Task 4- SETI
Answer the Following Questions on SETI Use the following information to help
-
1) What Does SETI Stand for
2) What is the role of SETI?
3) Explain how the Hubble telescope is useful to SETI
4) Why is "looking" for Signs of Life difficult?
5) Explain How we "listen" for signs of life.
6) In YOUR opinion is Listening or looking the best chance of finding life. Explain your answer
7) There are a number of vital things that the Earth has, which make it capable of supporting life. What are those things?
Evaluate your work
Task 5- Types of Radiation
Read the following information.
Using this information, produce a leaflet (on plain A4 paper) explaining the three types of nuclear radiation you must include information on.
- How radiation is emitted (what particles are involved)
- It's charge and mass
- Penetrative qualities
- What background radiation is
-
1. Name the three main types of nuclear radiation
2. List the three types of radiation in order of increasing penetrating power
3. List the three types of radiation in order of increasing ionising ability
4. What is the mass of an alpha particle? (in "atomic mass units")
5. What is the mass of a Gamma ray?
6. Will a piece of paper stop Beta particles?
7. A piece of Americium-241, at room temperature, emits 200 a particles per second. How many will it emit each second when it is heated to 150 degrees Celsius?
- HIGHER ONLY:-
- 1. What happens to the atomic mass and the atomic number
of a nucleus when it emits a Gamma particle?
2. What happens to the atomic number of a nucleus when it emits a beta particle?
- Task 5c - Is it a goal? (not availabe online YET)
Task 6 - Half Life (HIGHER ONLY)
Answer the following questions in your exercise books, write the answers in such a way that You can see what question was. Use the information from here
-
1. Explain what is meant by the term half life
2. A material has a half-life of 3 hours. What fraction of the atoms will have decayed after 6 hours?
3. A researcher measures 200 counts per minute coming from a radioactive source at midday. At 3 o'clock, she finds that this has dropped to 25 counts per minute.< What is the half-life of the radioactive source? Explain How you worked this out
4. a) Draw a graph to show the decay of the following radioactive substance
| TIME (Hours) | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 |
| Activity (Bq) | 1280 | 640 | 320 | 160 | 80 | 40 | 20 |
- b) What is the half-life of this substance?
c) What was the activity count after 5 Hours?
d) What would the Activity count be after 16 hours?
- 5.
Use the graph to work out
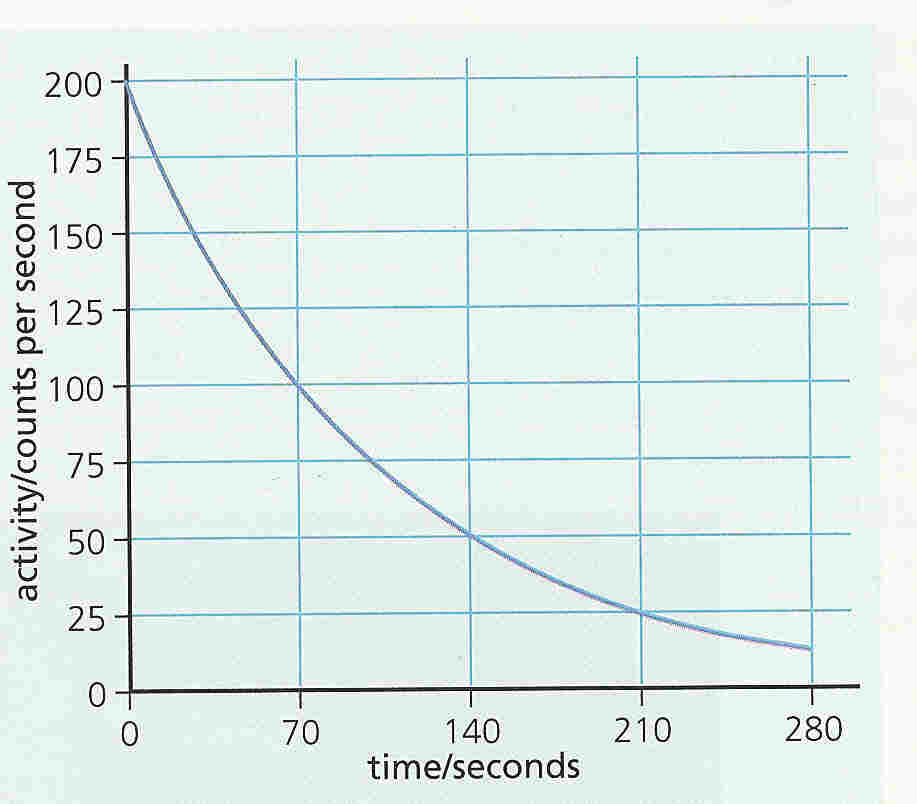
a) 200 counts to 100 counts
b) 150 counts to 75 counts
c) 120 counts to 60 counts
d) What do you notice about your answer to parts a b and c?
e) Explain your answer to part d, why has this happened?
Task 7 - Uses of Radiation
Read the information on "uses of radiation" here . Now, copy out these questions and then answer them
-
1. How can radiotherapy prevent cancer from spreading?
2. How do the doctors prevent HEALTHY cells being killed during radiotherapy?
3. Why are Alpha sources not used to check the thickness of paper as it comes out of a mill?
4. Which type of radiation is used for checking welds on aircraft parts? Explain why
5. In medicine, what is a Tracer?
6. Why is Technetium-99 a good tracer to use in medicine?
7. Why are cancer cells killed more easily than healthy cells by gamma rays?
8. Which type of radiation is used in domestic smoke detectors?
9. What does the radiation DO to the air in a smoke detector, so that a current can flow- use a diagram to help you explain?
10. Why do we use gamma rays to sterilise some medical equipment, rather than simply heat it to kill the bacteria?
11. Which isotope of carbon is used in radioactive dating?