PD6 EARTH SPACE AND RADIATION REVISION TOPICS
The Following topics are the MAIN areas of study for this unit for both Foundation and higher level candidates. It is advised that these areas should be revised in more depth.
AREAS OF STUDY
Solar System
Motion and Gravity
Distances in Space
Big Bang
Life Of stars
Red Shift
Basic Radiaition
Half Life
Effects and Uses of Radiation
Self teach module
Back to main Physics menu
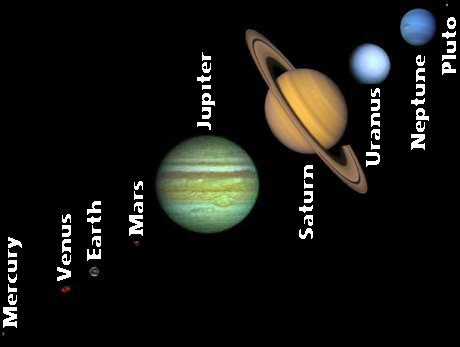
- Order of the nine planets
- Rotation of the earth to get day and night
- Tilt of the earth the reason we get seasons
- Which planet is biggest/smallest, hottest,/coldest, has most moons etc
back to top
| Acceleration |
= |
Change in Velocity |
÷ |
Time |
| Acc |
= |
D D |
÷ |
t |
| m/s2 |
|
m/s |
|
sec |
| Acceleration |
= |
Force |
÷ |
Mass |
| Acc |
= |
F |
÷ |
M |
| m/s2 |
|
(N) |
|
(kg) |
- Unless there is an opposing force an object moves in a stright line indefinately
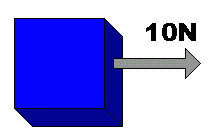
- an object moves in the direction of the largest force
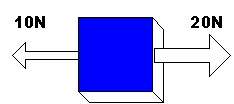
- an object stays still if the forces acting on it are balanced
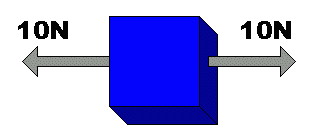 OR if there are no forces acting on it
OR if there are no forces acting on it
GRAVITY
- Affects weight (on Earth 1kg=10N)
- Size of gravity depends on size and density of object (e.g Earth has more gravity than the moon)
- Gravity is responsible for centripetal force that keeps planet orbiting sun and the moon orbiting the Earth
- Makes all objects accelerate towards earth at same rate (10m/s2)
- Heavier objects have higher terminal velocity see the previous unit for more information
back to top
Know the relative distances (in terms of which is biggest/ smallest distance)
- the planets to the sun,
- the moon to the earth,
- the sun to it’s nearest neighbours
LINK
Scale model of the solar system
- size of galaxy compared to solar system
- size of galaxy
back to top
Click here to view slide show of the Big Bang theory(power point needed)
of the Big Bang theory(power point needed)
- that the big bang is on of the most likely theories that might explain how the universe began
- Evidence that the big bang happened
back to top
- How a star is born (as gravity makes the hydrogen particles fuse)
- How long a star stays as a main sequence star (depending on size/ illuminosity)
- How a star "dies" (depending on it’s size)
back to top
Change in frequency as the detector moves towards or away from wave
- Doppler effect- sound (going towards sound wave frequency/pitch increases)
e.g. an Ambulance moving towards you sounds high pitched:-
If the Java applet below does not load you need a Java platform (an add on for windows explorer)
Download it here
b) Red shift- light (going toward light wave frequency increases so light looks bluer) eg stars moving away from each other appear redder
back to top
Click here for more information  on radiation
on radiation
Some Elements have isotopes that are unstable they are "radio active and might emit
- Alpha Radiation (a ) Helium nucleus emitted from nucleus of unstable isotope
Not very penetrative thick card can stop it vapour trails can be detected
- Beta Radiation (b ) electron emitted from nucleus of radioactive atom
Medium penetrative qualities can be stopped by a thick piece of metal
- Gamma Radiation(c ) Electromagnetic wave released from atom
Highly penetrative thick lead needed to stop it
- Can be detected by Geiger counter
back to top
Defined as the time it takes for a radio active material to fall to half it’s original value
Imagine a radio active material with a half life of 2 years. If it has a radioactive count of 1024/sec when it is brand new this is what happens to it
| Time |
New |
2 Years |
4 years |
6 years |
8 years |
10 years |
12 years |
14 years |
| Radio active count |
1024 |
512 |
256 |
128 |
64 |
32 |
16 |
8 |
this java script shows what happens to the radioactive particles inside the material as it "decays"
watch the "speed" at which the material decays to begin with. The decay then slows down as time goes on
If the Java applet below does not load you need a Java platform (an add on for windows explorer)
Download it here
back to top
USES OF RADIATION
Chemotherapy
Irradiating food
Measuring thickness of metals/check for metal defects
Nuclear power
Sterilising of surgical equipment
EFFECTS OF RADIATION
Effects vary according to level of dose and time exposed to it
Headaches/sickness loss of hair are exposure symptoms
Also linked to some cancers
back to top



 OR if there are no forces acting on it
OR if there are no forces acting on it