a plotting compass can also be used to show the magnetic field lines
a plotting compass can also be used to show the magnetic field linesThe Following topics are the MAIN areas of study for this unit for both Foundation and higher level candidates. It is advised that these areas should be revised in more depth.
 a plotting compass can also be used to show the magnetic field lines
a plotting compass can also be used to show the magnetic field lines you can make the field stronger by increasing the number turns OR Increasing the current
you can make the field stronger by increasing the number turns OR Increasing the current 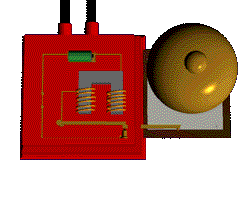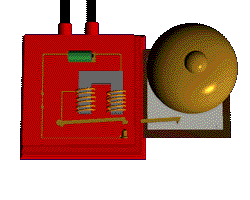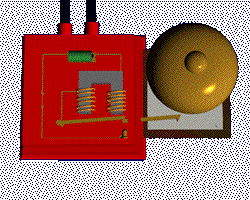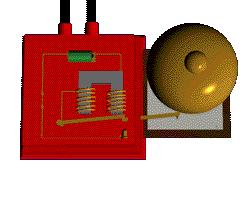
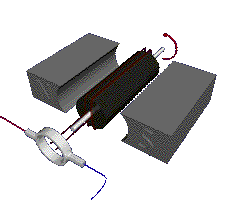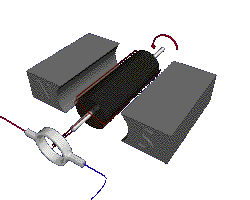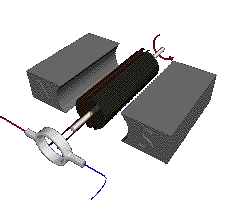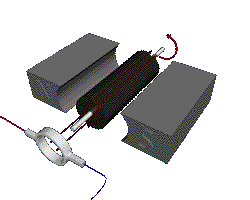
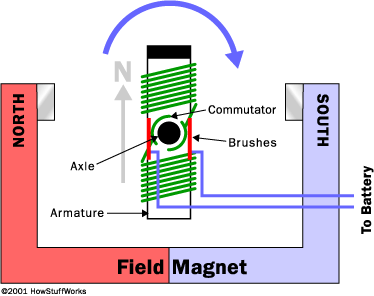
Putting an electromagnet near fixed permanent magnets makes the electromagnet (coil) move. This is the principal of a motor
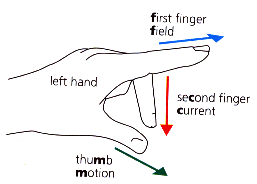
Parts of a motor
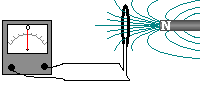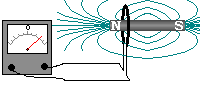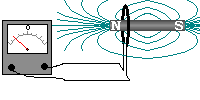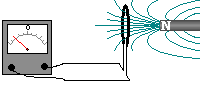 The same effect can be achieved if the coil is moved towards the magnet
The same effect can be achieved if the coil is moved towards the magnet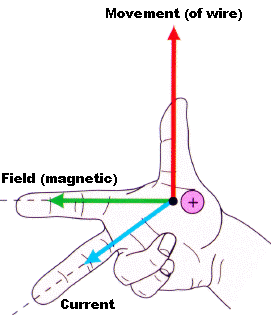
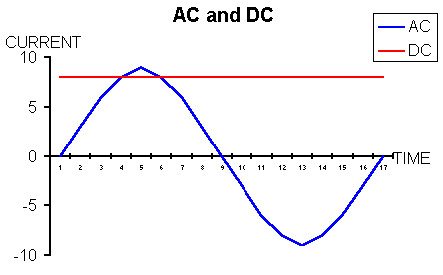
AC-Alternating current the sort of current you get from the mains (looks like sine wave)
DC Direct current- the sort you get from batteries (flat line)
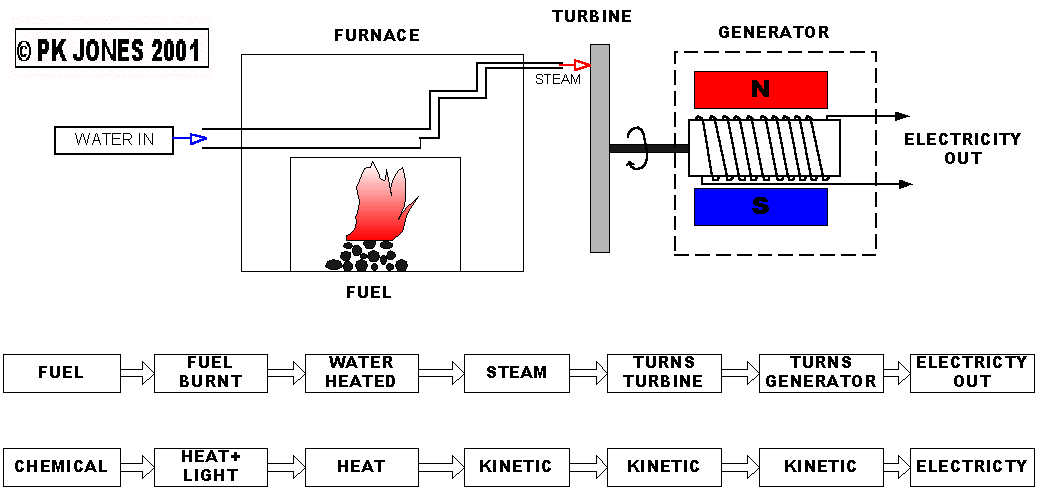
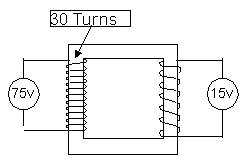
Only works on an a.c current
Primary coil current(amps) ¸ Secondary coil current (amps) = number of primary turns¸ number of secondary turns
| Potential Energy | = | Mass | × | Gravity | × | Height |
| pe | = | m | × | g | × | h |
| (j) | = | (kg) | (N/kg) | (m) |
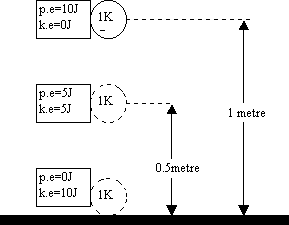 As the Object falls it gains Kinetic energy at expense of Potential energy
As the Object falls it gains Kinetic energy at expense of Potential energy
| Kinetic Energy | = | ( | Mass | × | Velocity˛ | ) | ÷ | 2 |
| k.e | = | ( | m | × | v˛ | ) | ÷ | 2 |
| (J) | (kg) | m/s) |

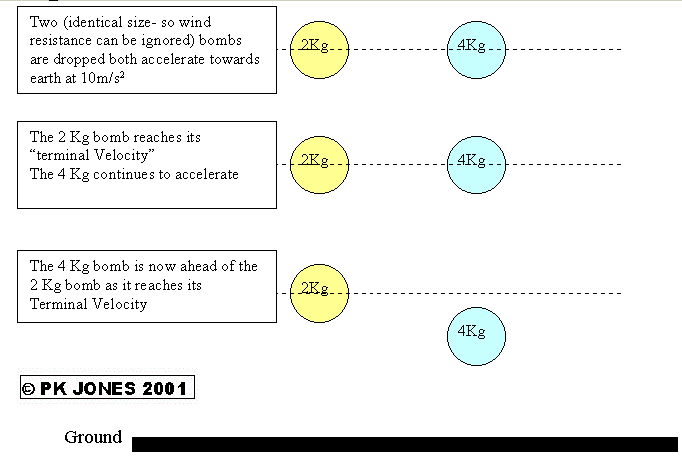
Work is done whenever a force moves an object over a distance
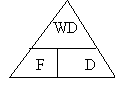
| Work Done | = | Force | × | Distance |
| WD | = | F | × | D |
| (J) or Nm | (N) | (m) |
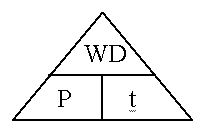
Rate at which WORK is done
| Power | = | Work Done | ÷ | Time |
| P | = | WD | ÷ | t |
| (w)or J/s) | (J)) | (sec) |
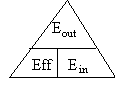
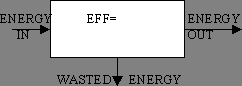
How much of the Energy put in is converted into USEFUL Energy
| Efficiency | = | USEFUL Energy Out | ÷ | Energy In |
| Eff | = | Eout | ÷ | Ein |
| no units | (J)) | (J) |