 >
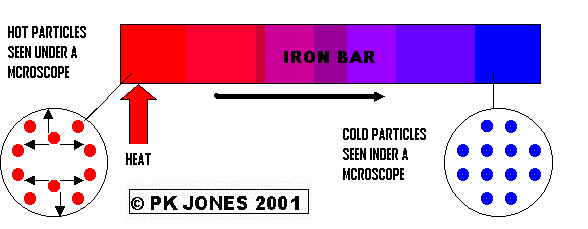
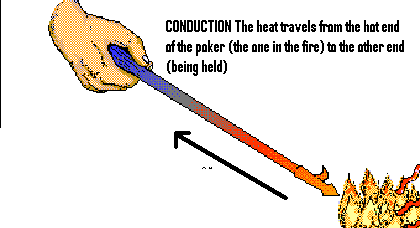
>This is the transfer of Heat in SOLIDS When the iron bar is cold the particles (viewed under a powerful microscope) don't move very much. However, when the heat is applied to the Iron Bar the heat energy changes into kinetic (moving) energy in the particles. This makes them bump into the particles around them. This makes the other particles move more, these then bump into the particles around them. This keeps happening (like a domino effect). Eventually, the heat energy is transferred through the iron bar in the direction of the black arrow
Example of Conduction
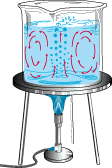
b)CONVECTION
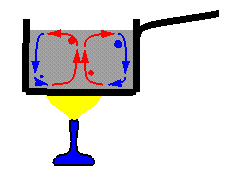
Convection is the transfer of heat in LIQUIDS AND GASES When the water is cold the particles are fiarly close together and relatively DENSE and heavy. However, When the Water is heated the particles move apart and so the water because LESS DENSE and hence lighter. The colder (denser) water at the top falls displacing the hot less dense water. So we get a CURRENT similar to the one shown above
c) RADIAITION
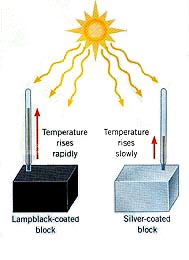
This is Heat transfer via Infra Red WAVES. (see The Electromagnetic-spectrum) No particles are involved so heat can travel through vacuums In addition, heat is ABSORBED by dark coloured materials and REFLECTED by light coloured materials