PD1 WAVES REVISION TOPICS
The Following topics are the MAIN areas of study for this unit for both Foundation and higher-level candidates. It is advised that these areas should be revised in more depth.
NB Those topics needed by Year 11 students for the
terminal exam are highlighted in blue
AREAS OF STUDY
Characteristics of Waves
Speed of a Wave
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Reflection, Refraction and Total Internal
reflection
Uses of Internal Reflection
Seismic waves
Ultrasound
Back to main Physics menu
Year 11 power point presentation on waves
and rays
Waves
Transfer ENERGY without transferring MATTER
Types of wave
a)Transverse
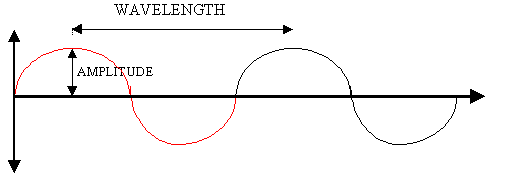
b)Longitudinal
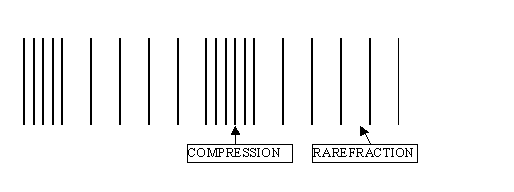
Use either:
a)
|
SPEED |
= |
DISTANCE |
¸ |
TIME |
|
S |
= |
D |
¸ |
T |
|
M/s
km/h or mph |
|
M km or
miles |
|
Sec or
hrs |
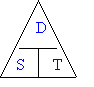
OR
b)
|
VELOCITY |
= |
FREQUENCY |
´ |
WAVELENGTH |
|
V |
= |
F |
´ |
l |
|
m/s |
|
Hz |
|
m |
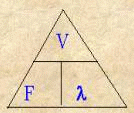
Speed of Light= 300,000,000 m/s Speed of sound (in air)=330m/s
Click here for
Information  on
the Electromagnetic Spectrum
on
the Electromagnetic Spectrum
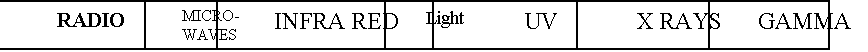
§
Know the ORDER of the Waves
§
Know the uses and dangers of each types of
Electromagnetic Wave
§
How Microwave Ovens work
§
How Microwaves and Infra red waves heat food
§
That Radio Microwave and Infrared are used to
carry Information
§
The Benefits of Using X-rays and Gamma rays in
Medicine (including using tracers)
4)
REFLECTION/REFACTION AND TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION
a)Law of reflection
angle of incidence = angle of
reflection
b) Refraction and total internal reflection
REFRACTION Apparent "bending
of light as it enters a material of different density
1) Entering a more dense material Slows down bends
towards normal
2) Entering a less dense material Speeds up bends
away from normal
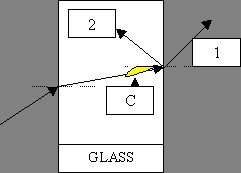
As Light leaves glass block it can either refract (1) or
totally internally reflect (2) depending on angle C
Smaller than 42 Light refracts
Bigger than 42 Light reflects
5)USES OF INTERNAL REFLECTION
1) FIBRE OPTIC CABLES
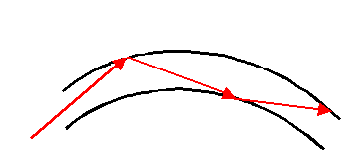
Information (such as Sound, TV Pictures etc) is converted into a Light signal and transmitted down a thin glass fibre, Since the Fibre is so thin Total internal reflection takes place (like shown above). Thus the signal can travel all the way down the fibre (no matter how long it is) without much signal loss
2) ENDOSCOPES


A Fibre optic cable with a very small camera attached to one end of a fibre optic cable. This can be inserted into a body through a small incision. The camera sends images through the cable to a viewer attached to the other end of the cable.
3) BIKE RELECTORS
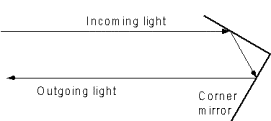
Each reflector has hundreds of small cube-corner elements. Each cube corner is effectively 2 mirrors at a 90 degree angle to one another, they reflect light back in the same direction it came from. As shown above
4) PERISCOPES
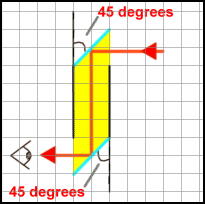
This is used for seeing OVER objects. It is simply made from 2 mirrors the light is directed by the mirrors into the users eye (like shown above)
5) BINOCULARS
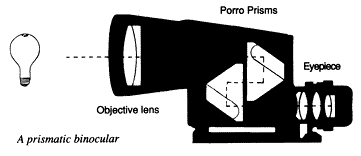
The Objective and eyepiece lenses magnify the image.
However Prisms are used to make the image appear the correct way up when it is
viewed. This is done by Total internal reflection within the prisms as shown
above
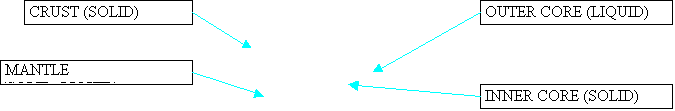
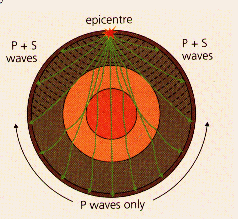
Caused by Earth quakes and plate movement
Detected by seismometers
P Waves (primary waves) are Longitudinal waves and fast moving they can travel through Liquid AND Solid so CAN travel through outer core
S Waves (secondary waves) are Transverse. They can ONLY travel through SOLID so CAN NOT travel through the outer core
This a a sound wave with a frequency beyond that of the upper range of human
hearing (above 20Khz). Although many Ultra sounds are well above that (e.g 1Mhz
is used in scans on pregnant women)
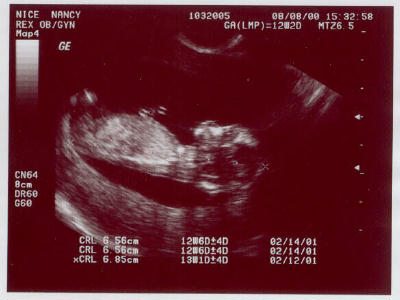
OTHER
USES:
- Cleaning
(the ultrasound shakes/vibrates dirt off the object)
- Breaking
down kidney stones in the body
- Sonar
(echoing/ searching under water)