PD3 FORCES AND MOTION REVISION TOPICS
The Following topics are the MAIN areas of study for this unit for both Foundation and higher level candidates. It is advised that these areas should be revised in more depth.
NB Those topics needed by Year 11 students for the terminal exam are highlighted in blue
AREAS OF STUDY
Speed And Velocity
Measuring Speed
Motion Graphs
Acceleration
Stopping Distances
Turning Forces
Back to main Physics menu
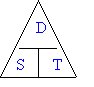
a) Speed
| Speed |
= |
Distance |
÷ |
Time |
| S |
= |
D |
÷ |
T |
| (m/s) (km/h) (mph) |
|
(m) (km) (miles) |
|
(secs) (hrs) |
b) Velocity
back to top
Ruler and Stopwatch
Computer and Light Gates
Ticker Tape timer
back to top
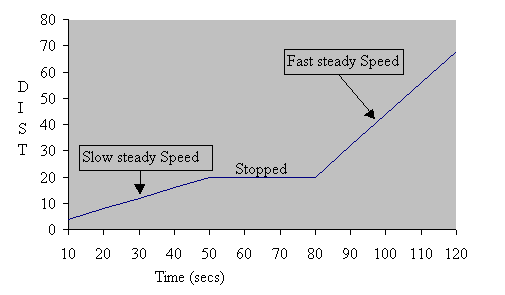
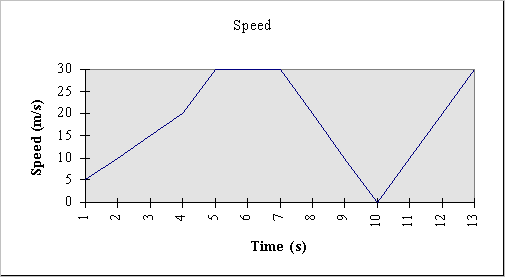
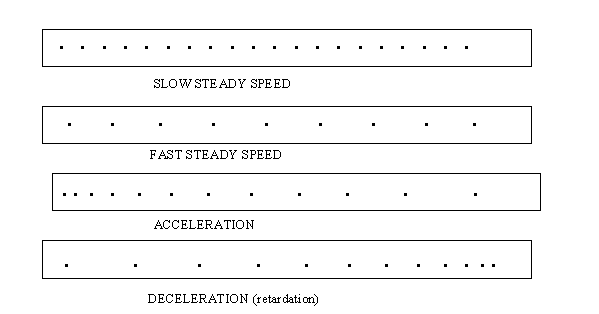
- Distance Time Graphs
Speed Time Graphs
back to top
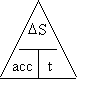
Is Rate at which speed increases.
Measured in m/s2
Either
a)
| Acceleration |
= |
Change in Speed |
÷ |
Time |
| A |
= |
D D |
÷ |
T |
| (m/s2) |
|
(m/s) |
|
(secs) |
Or
b) Newtons third Law
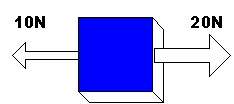
Acceleration increases with:-
INCREASED FORCE |
DECREASED MASS |
 |
|
| Acceleration |
= |
Force |
÷ |
Mass |
| Acc |
= |
F |
÷ |
m |
| (m/s2) |
|
(N) |
|
(kg) |
back to top
Stopping Distance = Thinking Distance + Braking Distance
HIGHWAY CODE STOPPING DISTANCES
SPEED |
THINKING
DISTANCE |
BRAKING DISTANCE |
OVERALL STOPPING DISTANCE |
20 mph |
20 ft. (6 m) |
20 ft. (6 m) |
40 ft. (12 m) |
30 mph |
30 ft. (9 m) |
45 ft. (14 m) |
75 ft. (23 m) |
40 mph |
40 ft. (12 m) |
80 ft. (24 m) |
120 ft. (36 m) |
50 mph |
50 ft. (15 m) |
125ft. (38 m) |
175 ft. (53 m) |
60 mph |
60 ft. (18 m) |
180 ft. (55 m) |
240 ft. (73 m) |
70 mph |
70 ft. (21 m) |
245 ft. (75 m) |
315 ft. (96 m) |
Things that effect stopping distances
| THINKING DISTANCE |
BRAKING DISTANCE |
| Age |
Road Conditions (water/ice etc) |
| Distractions |
Tyre Conditions/Inflation |
| Drugs/Alcohol |
Brake Conditions |
| Tiredness/Illness |
Weight of Veichle |
back to top
A Turning force (or Moment) is a force around a point (pivot)
The Size of the turning force depends on the pull(or pushing) force AND the Distance from the pivot
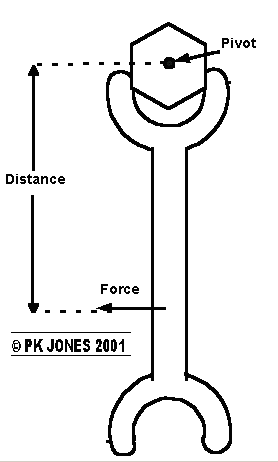
See saws have 2 turning forces (clockwise and anti-clockwise)
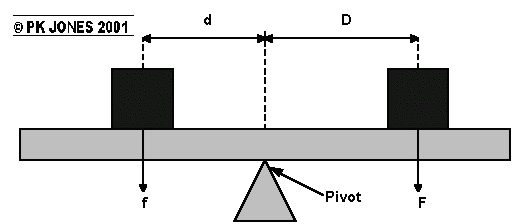
| ANTI CLOCKWISE MOMENT |
= |
CLOCKWISE MOMENT |
| f × d |
= |
F × D |
back to top